The study of International Political Economy is an attempt to utilise all major sources of academic discipline to break down, analyse, explain and predict complex real-world problems that transcend geopolitical and geographical borders. This comes from the realisation that the complexity of contemporary issues render it difficult to evaluate them solely on the basis of a single discipline and needs the indulgence of multiple branches of study. International Political Economy can be defined as a subject area or field of inquiry that looks into the tensions among states, markets and societal actors. With the expansion of the scope of the field, from international to transnational tensions, it has become more appropriate to rename it to “Global political economy”. The usage of this comprehensive term has therefore gained popularity to describe problems that go beyond classical security and economic challenges to include climate change, hunger and illicit markets worldwide. The study of International Political theory is therefore an evolving field. Its inherent dynamism is requisite to its survival and relevance.
Evolution of International Political Theory
Criticism conceived and propelled the evolution of IPE. The study emerged as an attempt at conciliation between the study of international politics and economy. The field gained traction with the emergence and growth of the global economy during the 1960s. Given the diverse nature of the field, it has evolved into an interdisciplinary field, adopting and utilising the resources from numerous diverse fields. Subjects like history, political science, sociology, international relations and economics have made remarkable contributions.
Post WWII developments in the international economy led to the birth of IPE. The next major development started with the end of the Cold war, where dissolution of the Soviet Union led to evolution of IPE. The Post Cold war era witnessed pronounced economic liberalisation, a surge in induction of nations into the global liberal order and widening of powers and scope of global institutions mandated to facilitate the growth of the emerging global economy. Further, this global shift towards embracing the ideals of liberalism and neoliberalism has led to the emergence of cracks in the foundation of these ideologies. The growth of the field in contemporary times is the result of deliberations, discussions and debates among and within the various schools of thoughts over these emergent cracks and fissures.
The field of enquiry constitutes two schools of thoughts, each stark opposites of the other: The rationalists, who are predominantly from the USA and the critical school of thought, who primarily represent the UK and the European nations.
Rationalists:
- Give prominence to interaction between states.
- Have evolved “sharply defined formal models and powerful quantitative tools” to work with and through the complexities of interstate trade and to understand the incentives for international collaboration.
- are Problem-solvers.
- Give equal importance to both theoretical and empirical work.
- Believe in the need for hegemony to maintain stability in the Global Economy.
- Favour creation of a framework to support and facilitate the creation of a hegemony to police and maintain order and adherence to law.
Critical School:
- Complained about and opposed the concept of hegemony and the hegemony of the USA in International relations and that of the rationalists in IPE.
- Point out dangers of hegemony.
- Problem-posers.
- Work produced is predominantly critical, normative and often focused on the structures of the global economy (global capitalism).
- Identity defined primarily as being antithetical to or highly critical of the rationalist school.
The criticisms of the liberal order post the cold war and the way in which the two schools took it up sets the stage for the development of IPE in the present era. Although the two schools have developed their analysis and theories under different, distinct styles, their main agenda has been the same. The unilateral response to the emergent fissures has been the metamorphosis into a study which better understands the nature of contemporary politics and economy. The two schools have, quite accurately identified the need to collate the fields of International Political Economy and Comparative Political Economy to produce a much more comprehensive and encompassing field of Global Political Economy. To achieve this objective, while the rationalists have followed primarily the modern approaches along empirical lines, the critical school has followed the normative approaches.
Theoretical perspectives key to the study of IPE:
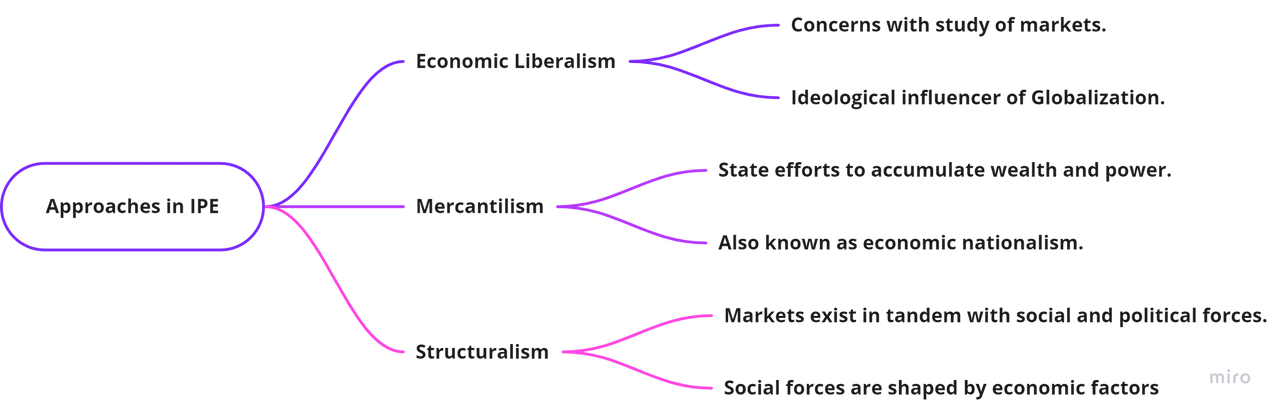

- Economic Liberalism: Propounded by Adam Smith, Keynes, Hayek and Friedman.
Support free markets and free trade.
Based on the assumption that under pure market conditions, humans behave rationally. - Mercantilism: Closely associated with the political philosophy of realism.
Central focus is the problem of security and the role of state in providing the same.
Focuses on state efforts to accumulate wealth and power, security of society from physical harm and external influences.
Theorizes two types of power – hard power and soft power. - Structuralism: Rooted in Marxism, but goes beyond it.
Looks at the issues in IPE by studying the impact of the dominant economic structure on different social classes.
Emphasize that markets have never existed in a social vacuum. The some combination of social, economic, and political forces establishes, regulates, and preserves them.
Finds the current capitalist system unfair and exploitative and demands its replacement with a system which undertakes a much more just distributive system.
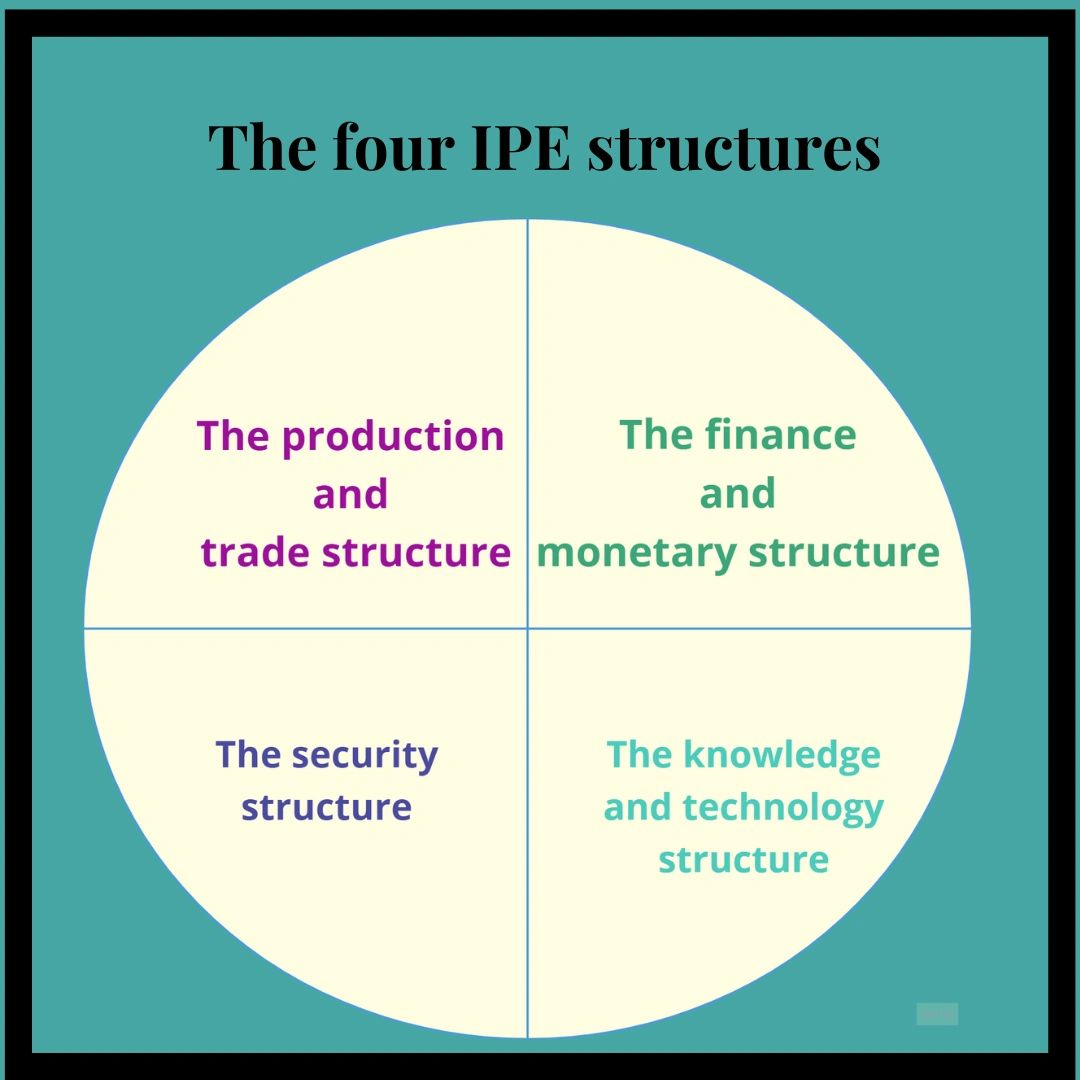
Susan Strange’s 4 structures of IPE
Conclusion
The future of the study of global political economy should focus on the collaboration and complementary combination of the two schools of thought. This will result in both of them imbibing the best of each other, the rationalists adopting normative methods of analysis and the critiques developing an identity of their own separate from that critical of the rationalists. However, the antithetical nature of the two should not be lost in this process of complementary combination. For, it is this opposing nature of the two schools that has resulted in the evolution of the field through the dialectic principles of growth.


Wow wonderful blog layout How long have you been blogging for you make blogging look easy The overall look of your site is great as well as the content
I do agree with all the ideas you have introduced on your post They are very convincing and will definitely work Still the posts are very short for newbies May just you please prolong them a little from subsequent time Thank you for the post
I understand. I will try to elaborate the ideas in these blogs.
Thank you for reading, and thank you for the feedback.
Hello Neat post Theres an issue together with your site in internet explorer would check this IE still is the marketplace chief and a large element of other folks will leave out your magnificent writing due to this problem